Human Toll of Jail Jail Populations Veterans November 10, 2022
Many veterans experience substance use disorders, mental health conditions including Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), and trauma, including traumatic brain injuries, all of which can lead to involvement with the criminal legal system. Fifty-five percent of veterans incarcerated in 2011–2012 reported having a mental health disorder, with mental illness diagnosis twice as high in veterans as in non-veterans. Approximately 65% to 71% of justice-involved Veterans had a reported substance use disorder before arrest.
In recognition of Veterans Day on November 11th, we would like to highlight several relevant resources and opportunities. A focus on specific populations, such as Veterans, aligns with the commitment Safety and Justice Challenge (SJC) communities have to diversion and deflection, as well as meeting the behavioral health needs of individuals who are or may become involved with the criminal legal system.
- Many SJC cities and counties, which receive support from the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, operate Veterans Treatment Courts, including Harris County, TX, Cook County, IL, Ada County, ID, and Palm Beach County, FL. Unlike traditional criminal courts, the primary purpose of a Veterans Treatment Courts is not to determine whether an individual is guilty of an offense, but rather to ensure that they receive treatment to address unmet clinical needs. There are over 600 Veterans Treatment Courts across the U.S.
- With the integration of the new three-digit National Suicide and Crisis Lifeline (988), people can now dial 988 and press 1 to access the Veterans Crisis Line. There are also options to chat online or text at 838255. Responders are trained in crisis intervention and military culture.
- One program from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) that allow entities to identify whether an individual has prior military service is the Veterans Re-Entry Search Service. This web-based system allows prison, jail, and court staff to identify Veterans quickly and accurately among their populations. The VA makes this service available to facilitate its own direct outreach to these Veterans, and to inform the development of Veteran-specific programs in the criminal legal system.
- Veterans Justice Outreach specialists provide a range of services to assist justice-involved Veterans, including outreach to Veterans across the possible span of their interactions with the criminal legal system, such as law enforcement encounters, courts, jails, and prisons. The aim of the Veteran Justice Outreach program is to avoid the unnecessary criminalization of mental illness and extended incarceration among Veterans by ensuring that eligible, justice-involved Veterans have timely access to Veterans Health Administration services. Each state has one or more Veteran Justice Outreach specialists who can provide additional information on the program.
- The Peer Specialist Toolkit helps Veterans Health Administration medical centers hire and deploy peer specialists who help other Veterans get treatment for mental and substance use disorders.
- The Rural Veteran Outreach Toolkitassists VA personnel in collaborating with community partners to reach rural Veterans through education and outreach.
- The National Institute of Corrections’ Veterans Reentry Programming: Supporting Transition to Civilian Life Across the Sequential Intercept Model outlines Veteran-specific reentry approaches.
We also operate SAMHSA’s Service Members, Veterans, and their Families Technical Assistance (SMVF TA) Center, which serves as a national resource to support states, territories, and local communities in strengthening their capacity to address the behavioral health needs of military-connected individuals and families. The SMVF TA Center supports specific initiatives like the VA/SAMHSA Governor’s and Mayor’s Challenges to Prevent Suicide among SMVF as well as the public at large through a variety of technical assistance efforts including needs assessments, virtual and onsite consultation, Policy and Implementation Academies, interagency collaboration and support, and dissemination of educational resources including a monthly e-newsletter.
One offering from the SMVF TA Center is the Crisis Intercept Mapping (CIM) for SMVF Suicide Prevention. The Crisis Intercept Mapping is a tool that helps community stakeholders visualize how SMVF flow through the crisis care system. The Crisis Intercept Mapping has some parallels to our Sequential Intercept Model and is designed to help communities strengthen the delivery of evidence-based suicide prevention policies and practices for SMVF before, during, and after a time of crisis.
As identified on the model below, within a community crisis system there are four key “intercept points” that provide opportunities for diverting at-risk SMVF to appropriate and effective prevention and support services:
- First Contact
- Acute Care
- Care Transitions
- Ongoing Treatment and Recovery Support
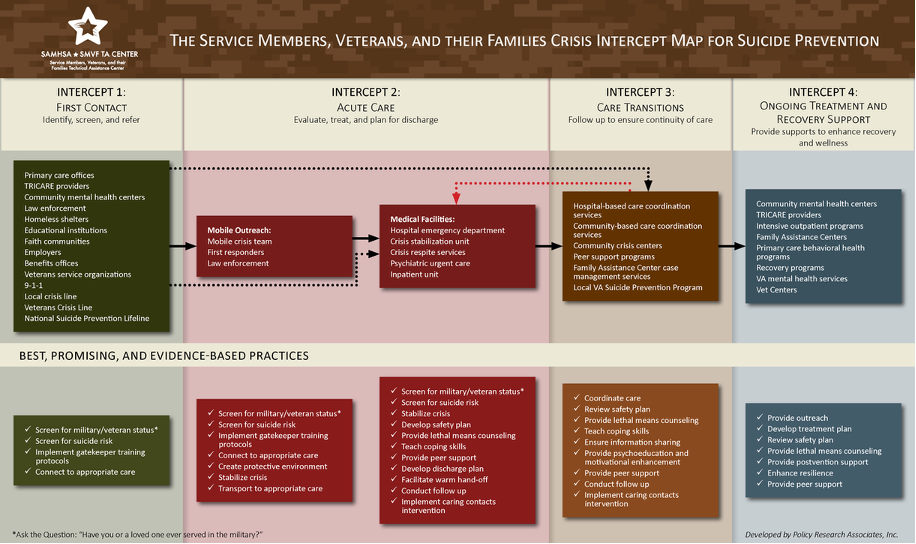
In 2022, the White House released a report, Reducing Military and Veteran Suicide: Advancing a Comprehensive, Cross-Sector, Evidence-Informed Public Health Strategy, directly calling for the “expansion of SAMHSA’s crisis mapping initiative to assist cities and counties in identifying gaps and incorporating best practices in suicide prevention for veterans interacting with community crisis systems” (Priority Goal 2 on page 13). Crisis Intercept Mapping is designed to bring together an interagency group of key stakeholders from the community to identify barriers and gaps in the community’s crisis system serving SMVF and discuss ways in which best practices and partnerships can be implemented to close those gaps and reduce service member and Veteran suicide through the development of integrated local strategic action plans.









